What is a Spread in Forex Trading?
After learning about what Forex is and the currency pairs traded in the Forex market, this lesson focuses on the concept of spread in Forex.
The spread is one of the key terms in Forex trading. Before delving into its explanation, we will first outline the mechanism of trading currencies in buying or selling, followed by the bid price and the ask price, and then explain what the spread is, as well as the size of trades and contracts in Forex.
We will cover the following topics in this article:
The Mechanism of Trading in Forex
Trading in the Forex market is exciting and one of the main advantages of the currency market is that it allows traders to trade in both directions—whether prices are rising or falling. Traders can buy in a rising market and sell in a falling market, unlike the stock market, where it is common to buy shares at a lower price and make a profit by waiting for a rise, then selling at a higher price.
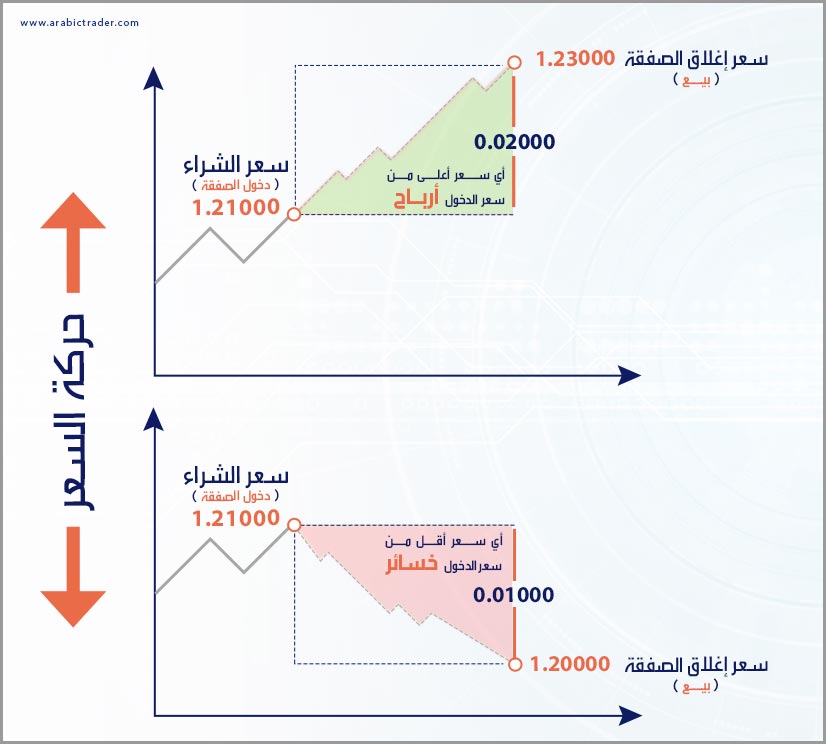
In the case of buying: A trader purchases a currency pair when they expect the exchange rate of one currency to rise against another. For example:
If you expect the Euro to rise against the US Dollar (EUR/USD) from 1.2100 to 1.2300, you would buy to benefit from this rise. Thus, you are buying Euros (EUR) and selling US Dollars (USD). If the price rises as expected, you will make a profit; if it falls contrary to expectations, you will incur losses.
In the case of selling: A trader sells a currency pair when they expect the exchange rate of one currency to fall against another. For example:
If you expect the Euro to fall against the US Dollar (EUR/USD) from 1.2100 to 1.2000, you would sell to benefit from this anticipated decline. Thus, you are selling Euros (EUR) and buying US Dollars (USD). If the price falls as expected, you will make a profit; if it rises contrary to expectations, you will incur losses.
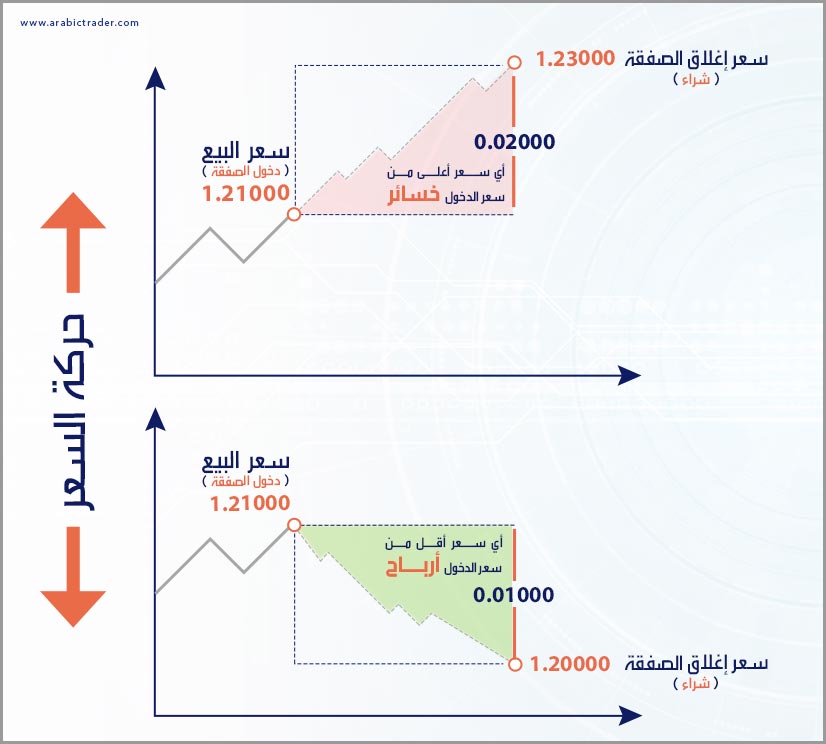
Some may wonder how to sell the EUR/USD pair if they haven’t purchased it initially. Here, we explain that you borrow Euros to sell them against Dollars, which is one of the significant advantages of the currency market.
Bid Price and Ask Price
In Forex trading, there are always two prices for each pair: the bid price and the ask price.
- Bid Price: This is the price a trader sees on their trading platform when they are selling in Forex or any other financial market.
- Ask Price: This is the price a trader sees on their trading platform when they are buying in Forex or any other financial market.
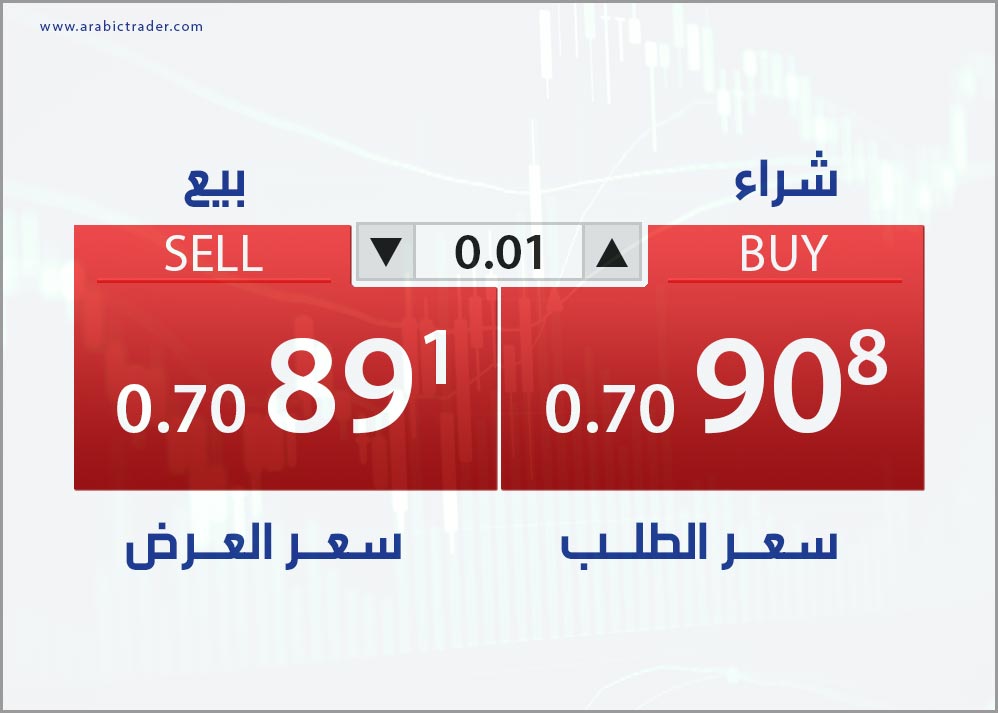
Understanding the relationship between these two prices is essential for making informed trading decisions. The bid price represents the maximum price that a buyer is willing to pay for a currency, while the ask price reflects the minimum price a seller is willing to accept. The difference between these two prices, known as the spread, is what brokers earn from facilitating trades. A narrow spread indicates high liquidity and low transaction costs, which can be advantageous for traders looking to maximize profits. Conversely, a wider spread may suggest lower liquidity and higher trading costs, highlighting the importance of choosing a broker with competitive pricing to enhance overall trading performance.
The Spread in Forex Trading
The spread is the difference between the bid price and the ask price. The ask price is always slightly higher than the bid price, and this difference is known as the spread. The spread is determined by the volume of available bids and asks in the Forex market or any other financial market like stock exchanges.

The spread represents the profit margin earned by the party executing the trade, whether it is a Forex brokerage, bank, or currency exchange office. The wider the spread between the ask and bid prices, the higher the transaction cost for the trader. Therefore, the spread is one of the essential criteria in choosing a good trading broker.
The following video explains the concept of the bid and ask prices and the spread between them, as well as how to navigate the market through them.
How is the Spread Calculated in Forex?
As mentioned earlier, the spread is the difference between the ask and bid prices. Typically, the spread is determined by the volume of bids and asks; the greater the volume for a specific pair, the lower the spread due to the high liquidity in the Forex market. Traders do not need to calculate this manually, as trading platforms calculate the spread automatically.
Let’s take an illustrative example from the MetaTrader 4 trading platform:
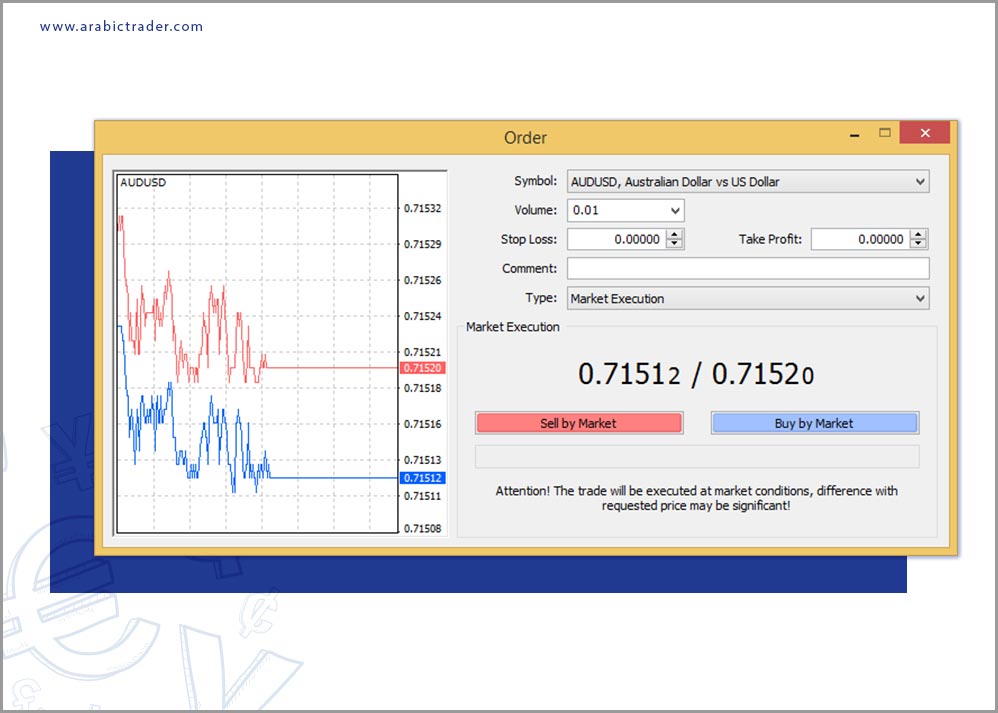
In this example, we open a trade on the AUD/USD pair, and as shown in the execution box, there are two exchange prices. The first price is 0.71520, which is the ask price, above the button for opening a buy order for the pair. The other price is 0.71512, which is the bid price, above the button for opening a sell order for the pair.
What is the Unit of Measurement for the Spread?
The spread is measured in a unit called a "pip," which is the smallest movement in the price of a currency pair. A pip is typically the fourth decimal place in a currency price, with some exceptions, such as currency pairs that include the Japanese yen, where a pip is calculated at the second decimal place. The term "PIP" stands for "Percentage In Point," indicating the percentage change represented in a pip. We covered the details of what a pip is in another educational article.

Conclusion
Understanding the spread is crucial for Forex traders, as it directly impacts the cost of trading and potential profitability. By grasping how spreads work and how they are calculated, traders can make more informed decisions and optimize their trading strategies.
The spread is the difference between the bid and ask prices for a currency pair, representing the cost of trading.
The spread is calculated based on the volume of bids and asks; higher liquidity typically results in lower spreads.
Understanding the spread is important as it affects the overall cost of trading and can impact profitability.
A pip is the smallest unit of price movement for a currency pair, typically representing the fourth decimal place in most pairs.


