What Is Blockchain and How Does It Work?
Blockchain technology has become a hot topic today, evolving into a cornerstone for record-keeping systems worldwide, especially with the rise of digital currencies. It was only launched about ten years ago by unknown individuals behind the creation of the first and most famous cryptocurrency, Bitcoin (BTC). In this article, we will explore the concept of blockchain technology, how it works, and why it has garnered such significant attention since its inception.
We will discuss this topic through the following points:
Historical Overview of Blockchain Technology
The idea of blockchain technology began in 1991 when Stuart Haber and Scott Stornetta first described the concept of creating a chain of encrypted, recorded data blocks. Later, computer scientist Nick Szabo attempted to implement this idea to create a decentralized digital currency named Bit Gold around 1998.
The real breakthrough for blockchain technology occurred in 2008 when developers under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto released a white paper to establish the blockchain model. A year later, it was practically applied as a comprehensive transaction ledger using the Bitcoin cryptocurrency.
In 2014, a significant technological leap occurred with blockchain, separating it from currency and exploring its potential for financial transactions among various parties. This led to the creation of Blockchain 2.0, which entered applications beyond digital currencies, such as what Ethereum offered in computer programs in the form of blocks representing financial instruments like bonds, now known as smart contracts.
What is Blockchain?
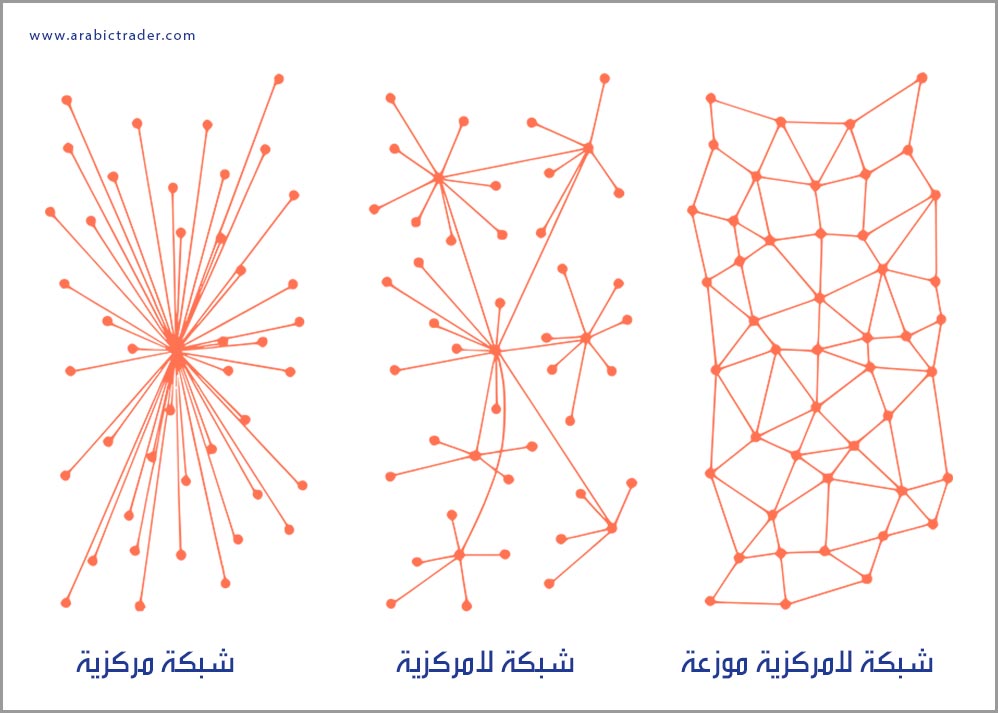
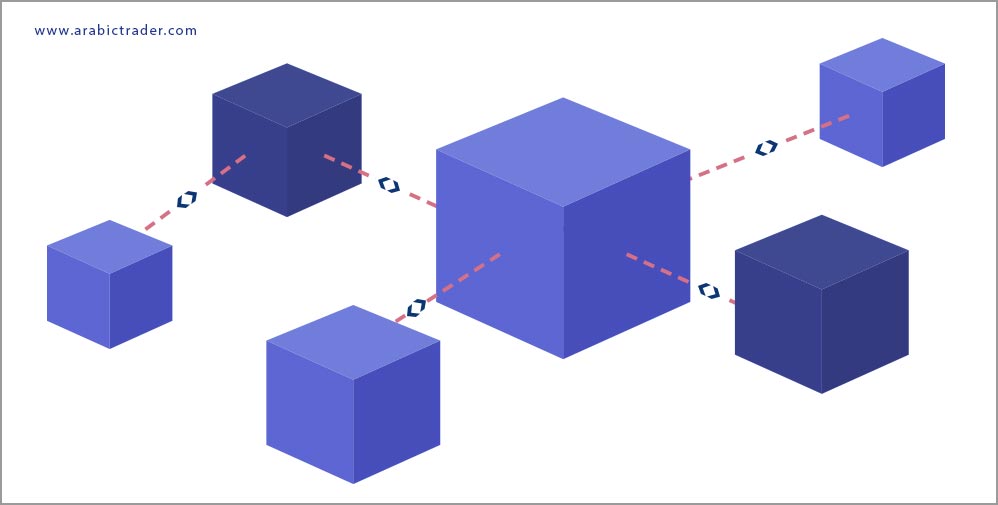
Blockchain is an open-source, programmable technology that is decentralized and secure. At its core, it is a digital ledger of transactions that is replicated and distributed across the entire network, comprising encrypted record blocks. Each block is linked together and secured using cryptography, containing a hash—a mathematical algorithm that records a small portion of the transaction data included in the overall ledger.
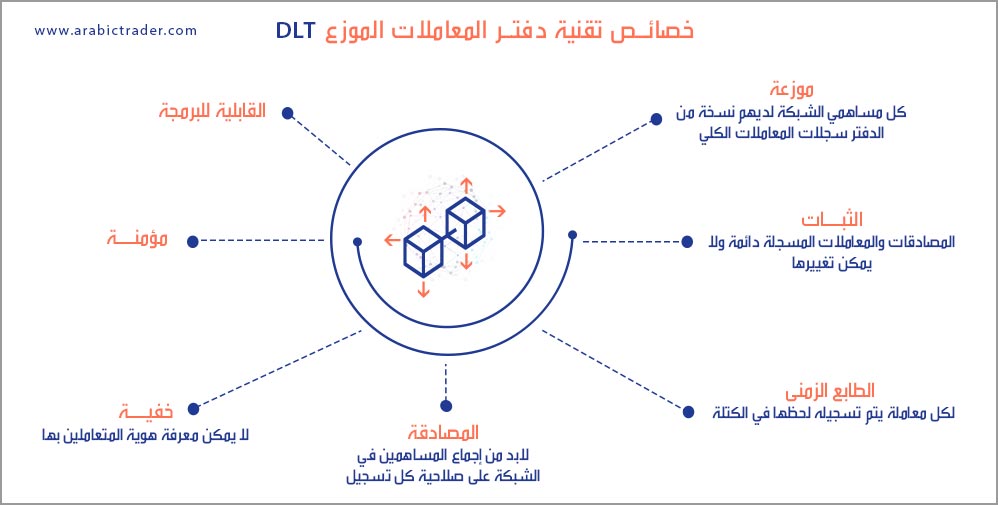
This decentralized database, managed by multiple participants, is referred to as Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT).
In essence, blockchain technology operates similarly to torrent files but in a more complex manner, utilizing sophisticated mathematical algorithms requiring powerful computing processors. This integrated network prevents risks related to centralized data storage.
To simplify this concept, consider the following example:
Imagine we have four individuals: Ahmed, Mohammed, Islam, and Omar. Each has a number of digital currencies, and Ahmed wants to buy an item from Mohammed for 0.12 Bitcoin. This means Ahmed will access his digital Bitcoin wallet and send Mohammed 0.12 Bitcoin in exchange for the item—this is referred to as a transaction.
This transaction must be recorded in the transaction ledger shared among the four individuals. The storage unit divides the record of the transfer from Ahmed to Mohammed into four encrypted partial copies and sends them to the records of Ahmed, Mohammed, Islam, and Omar. Each can read the record and know that 0.12 Bitcoin was transferred from one person to another without knowing the sender or receiver's identity—Islam and Omar are aware that a transfer occurred, but they do not know Ahmed is the sender and Mohammed is the recipient.
This means each of them possesses a small encrypted data share, allowing them to see all recorded transactions simultaneously without decrypting them or identifying the source of each transfer. All this occurs through the complex communication network managed by the Bitcoin software.
Applications of Blockchain
Blockchain applications function like traditional software applications but are executed through a decentralized architecture aimed at creating a secure economic or financial environment. Their primary goals are to enhance security, build trust, and encrypt assets through a reward system for miners in the network.
Blockchain’s capabilities become evident in banking and finance, where financial institutions replace traditional paperwork with a blockchain-based system. The benefits include reduced human friction and delays, increased operational efficiencies, and improved global business transactions, financing, auditing, settlement, banking, lending, and other transactions.

Additionally, as a database, blockchain can aid healthcare and insurance in enhancing patient data security while facilitating record sharing among service providers, recipients, and researchers. The increased security, transparency, and ease of tracking data within the network, along with its immutability, bolster trust between service providers and recipients.
Benefits and Advantages of Blockchain
Blockchain technology has gained credibility in business due to its ongoing development and robust advantages, including high security, transparency, data traceability, and cost-effectiveness while maintaining high efficiency. Here are five key benefits of blockchain technology:
-
Enhanced Security
When data is sensitive and critical, such as financial information, blockchain can significantly change how vital information is presented by creating an immutable, end-to-end encrypted record that helps prevent fraud and unauthorized activities. Privacy issues can also be addressed by anonymizing personal data and using permissions to restrict access. Information is stored across a network of computers rather than on a single server, making it difficult for hackers to access the data. -
Transparency
Blockchain utilizes a distributed ledger where transactions and data are recorded symmetrically in multiple locations. All authorized participants in the network see the same information simultaneously, providing complete transparency. Moreover, all transactions recorded in blocks are immutable, timestamped, and date-stamped, ensuring a documented timeline. This allows members to view the complete transaction record in precise chronological order, effectively eliminating any opportunity for fraud.![]()
-
Instant Traceability
Blockchain creates an audit trail documenting the source of the asset at every step in the registration and block formation process. This enables direct and easy access to data regarding the source. Traceability data can also reveal weaknesses in the chain. -
Increased Efficiency and Speed
Traditional paper-based processes are time-consuming, labor-intensive, and prone to human error, often requiring third-party mediation. By streamlining these processes using blockchain, transactions can be completed more swiftly and efficiently. Documents can be stored on blockchain along with transaction details, eliminating the need to exchange physical papers. There’s no need to reconcile multiple records, making auditing and settlement much faster. -
Automation
This involves automating the system; transactions can even be automated through smart contracts, further enhancing efficiency and speeding up processes. Once predefined conditions are met, the next step in the transaction or process automatically triggers. Smart contracts reduce human intervention and reliance on third parties to verify compliance with contract terms. For instance, once a customer submits all required documents for a claim, the claim can be settled and paid automatically.
The Role of Blockchain in Bitcoin Transactions
As mentioned earlier, blockchain technology is the foundational technology for Bitcoin, serving as the primary ledger for its transactions. Its role is to ensure the verification and updating of true records, where each node in the network performs mutual audits and communicates with each other to ensure all copies are consistent across all blocks. This process allows for the publishing and validation of all transactions of the digital currency.
Each Bitcoin transaction must be added to the blockchain records to be considered complete or valid. Transaction validation and inclusion in the blockchain are performed by miners, powerful computers that form and connect to the network.
Bitcoin is recorded to specific addresses. Creating an address involves encrypting a private key for Bitcoin, computed in fractions of a second. It’s essential to note that there is an enormous number of keys available for all transactions and currencies, making them impossible to break.
Anyone wanting to spend or transfer Bitcoin must have the private key, signing the transaction digitally. The network verifies the transaction using the public key, completing the transaction.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the way we think about data storage and transaction verification. Its decentralized nature enhances security, transparency, and efficiency across various industries, particularly in finance and beyond. As we continue to explore its capabilities, the importance of blockchain in facilitating cryptocurrency transactions, such as Bitcoin, cannot be overstated. Understanding its principles and applications will be crucial for anyone looking to navigate the future of digital currencies and decentralized technologies.
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring the information is secure, transparent, and immutable.
Blockchain works by creating blocks of transaction data that are encrypted and linked together. Each block contains a hash of the previous block, forming a secure chain.
Blockchain has various applications beyond cryptocurrency, including supply chain management, healthcare data management, and digital identity verification.
The benefits of blockchain include enhanced security, increased transparency, improved efficiency, and reduced costs, making it an attractive option for various industries.